Shoulder Joint Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
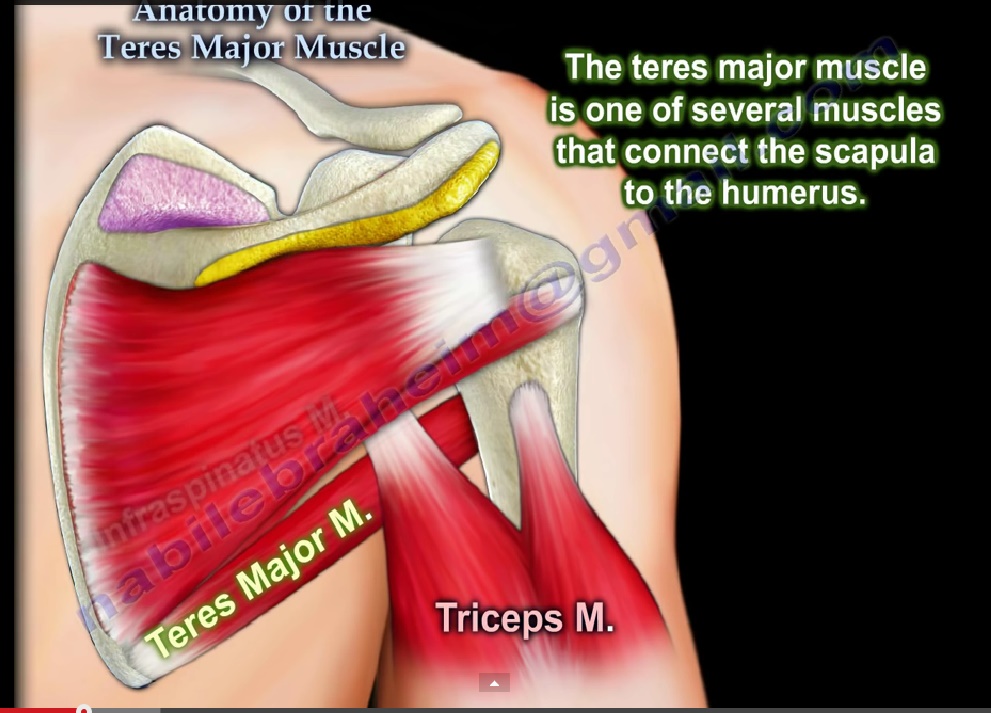
Teres major muscle (Musculus teres major) The teres major is a thick muscle of the shoulder joint. It spans from the inferior aspect of the scapula to the proximal part of the humeral shaft. Unlike the teres minor, the teres major muscle does not attach to the capsule of the glenohumeral joint. Thus it is not regarded as part of the rotator.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/teres-major-muscle/mXYmza3uHKGP5Q4FPNpog_musculus_teres_major.png)
muscle connection anatomy
Teres Major Anatomy Palpation. Palpating the teres major is an essential technique for clinicians to assess its condition and identify potential issues. To palpate the teres major, the patient should be in a seated or lying position, with the arm slightly adducted and medially rotated.
Anatomy Of The Teres Minor Muscle —
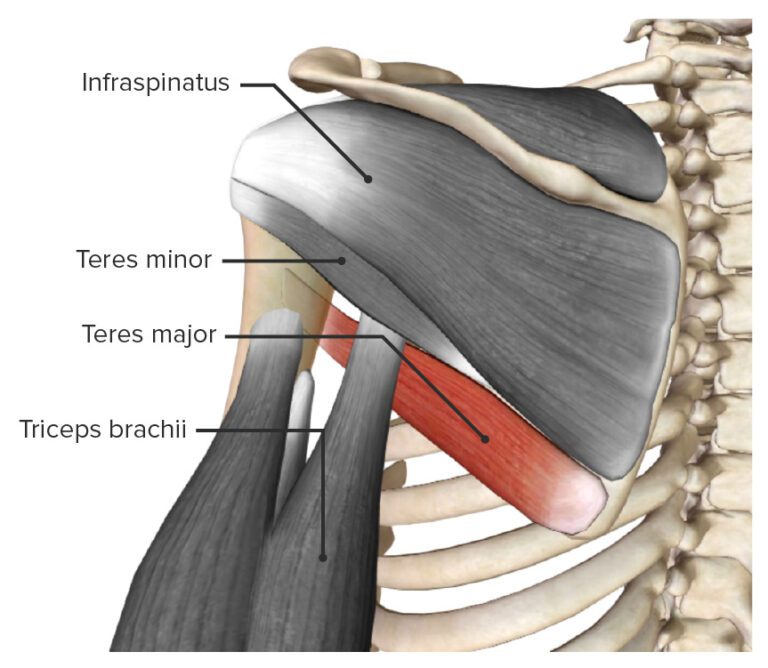
The teres major muscle is found in the shoulder region. It is a thick, fusiform type of skeletal muscle. It is located: - anterior (deep) to the long head of triceps brachii muscle; - posterior (superficial) to the scapula, coracobrachialis muscle; - superior to the latissimus dorsi muscle; - inferior to the teres minor and infraspinatus muscles.
Teres major muscle hires stock photography and images Alamy
If your teres major is overactive/short, do the following: Reduce your training volume on teres major exercises and lat exercises. If your overhead range of motion is limited, avoid vertical push exercises like the overhead press. Do high-incline push exercises instead (e.g. shoulder press on 60-75° incline).

Teres Major Origin, Insertion, Action The Wellness Digest
ANATOMY. Teres Major. Origin. Dorsal surface of inferior angle of scapula. Insertion. Medial lip of intertubercular groove of humerus. Action. Adducts and medially rotates arm. Innervation.

Latissimus dorsi Musculus teres major Musculus teres minor Muskelherkunft und Insertionsanatomie
The teres major is a thick but flattened, rectangular muscle that extends from the inferior posterior scapula to the medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus. It functions synergistically with the latissimus dorsi to extend, adduct, and internally rotate the humerus. Although the lati.
Anatomy of the Teres Major —
In this video we go over the anatomy facts of the teres major muscle: origin, insertion, innervation and function. Test yourself in our arm and shoulder musc.

Anatomy Of The Teres Major Orthopaedicprinciples Com Gambaran
Origin: Posterior aspect of the inferior angle of the scapulaInsertion: Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerusArtery: Subscapular and circumflex scapular arteriesNerve: Lower subscapular nerve (segmental levels C5 and C6)Action: Internal rotation of the humerus Description: The Teres major is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle, which arises from the oval area on the dorsal.

The Teres Major Muscle, Its Attachments and Actions Yoganatomy
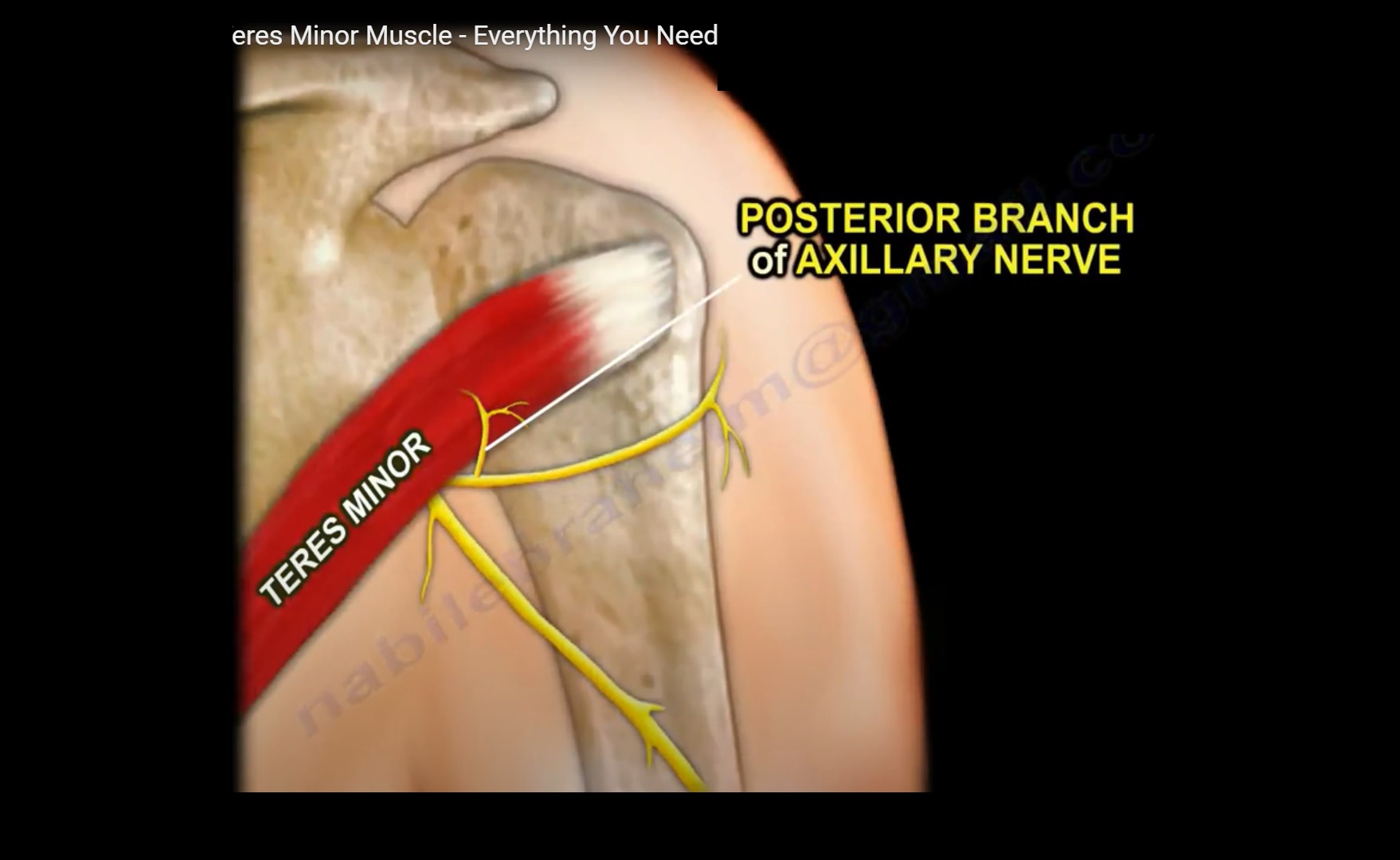
Actions: Adduction, extension and medial rotation of the upper limb at the shoulder. Innervation: Lower subscapular nerve. Blood supply: Thoracodorsal artery, posterior circumflex humeral artery. The teres major is an intrinsic muscle of the shoulder region. It forms the inferior border of the quadrangular space - the space that the axillary.

Teres Major Muscle Origin, Insertion & Action Human Anatomy Kenhub YouTube
Teres major. Media (1) The teres major (Latin: musculus teres major) is a flat and thick muscle of the upper limb. It stretches between the scapula and humerus. As the teres major muscle provides movements at the shoulder joint, it is classified as the muscle of the shoulder region. Muscles of shoulder region by Anatomy Next. Teres major. Origin.

15 Teres Major And Teres Minor Strengthening Exercises SET FOR SET
Dr. Ebraheim's educational animated video describes the anatomy of the Teres Major muscle.Origin & insertion: the teres major muscle arises from the dorsal (.
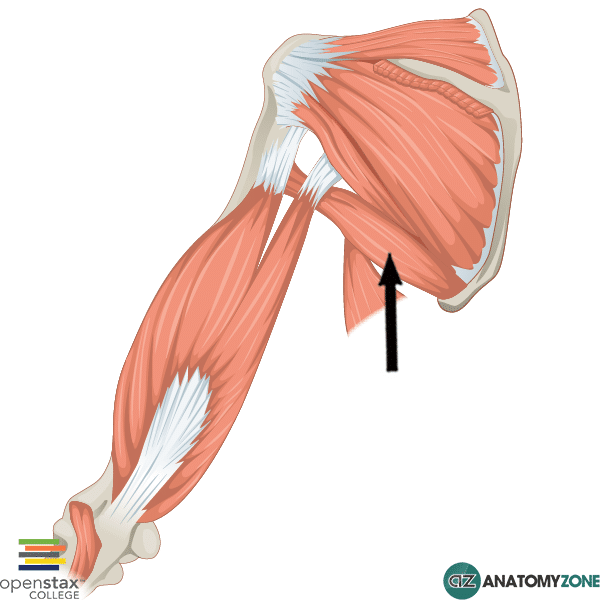
teres major Archives AnatomyZone
The teres major is a thick but flattened, rectangular muscle that extends from the inferior posterior scapula to the medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus.[1][2] It functions synergistically with the latissimus dorsi to extend, adduct, and internally rotate the humerus.[3] Although the latissimus dorsi and teres major muscles often function in conjunction with one another.
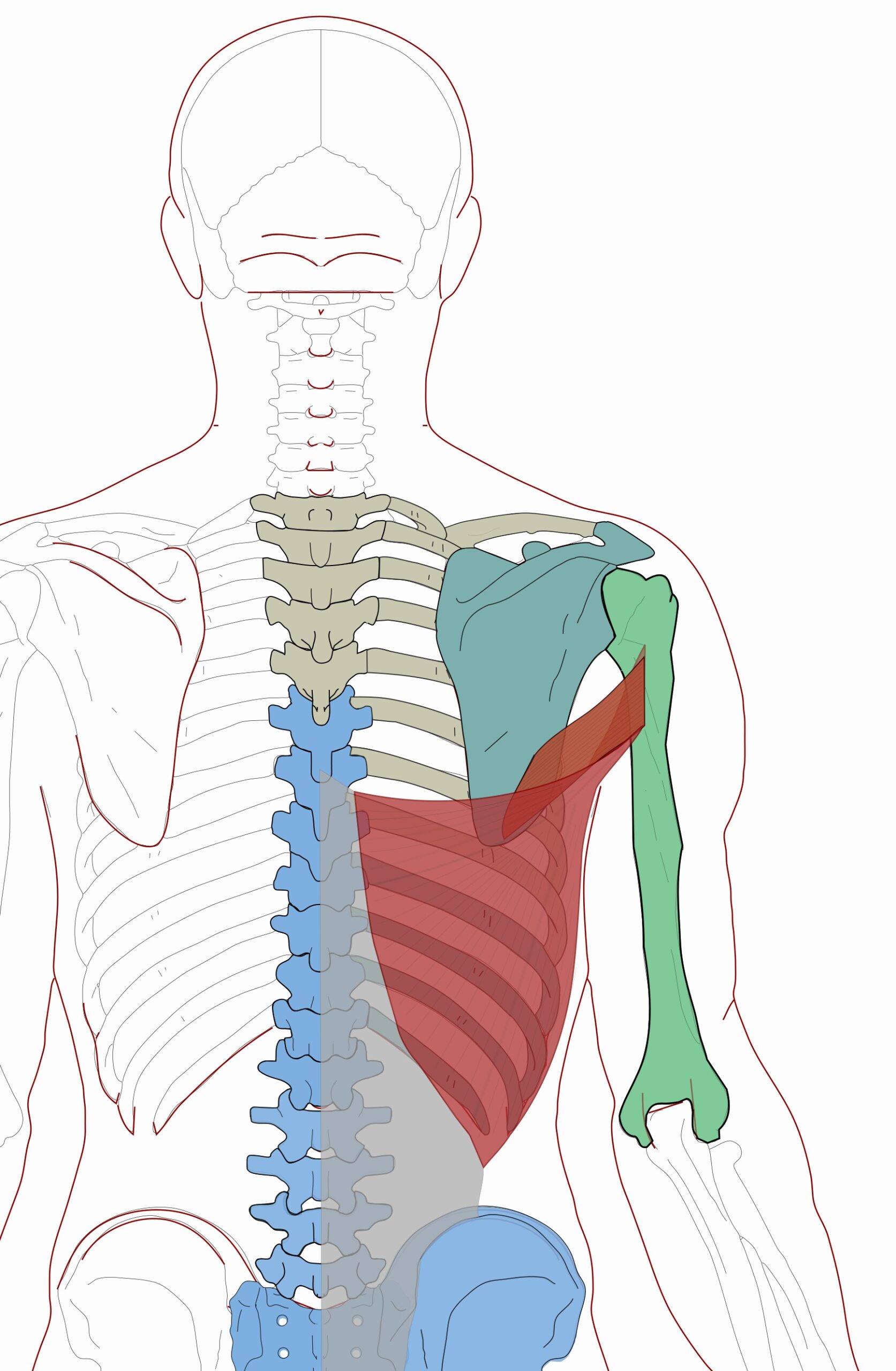
Teres Major Functional Anatomy Integrative Works
Teres Major injuries result in pain and difficulty with activities that require sideways or backwards movements with the arm. Isolated tears of the teres major are quite uncommon, but may occur in baseball or cricket players, especially pitchers and bowlers.; The main symptom of a teres major tear is a sudden sharp pain in the shoulder, upper arm and armpit.

The Teres Major Muscle
Gross anatomy. The muscle originates from the dorsal surface of the inferior angle of the scapula and inserts on the medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus. It is related to the latissimus dorsi muscle which wraps around the lower border of teres major. The tendon of the teres major lies posterior to the tendon of the.

Teres Major Muskeln Isoliert Schulter Anatomie Posterior Ansicht Auf Schwarzem Hintergrund
Structure. The Teres major muscle is composed of muscle fibers arranged in parallel and is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve (C5-C6). The teres major muscle is covered by a thin layer of fascia, which is a type of connective tissue that surrounds and separates muscles. It is also surrounded by a number of other shoulder muscles.
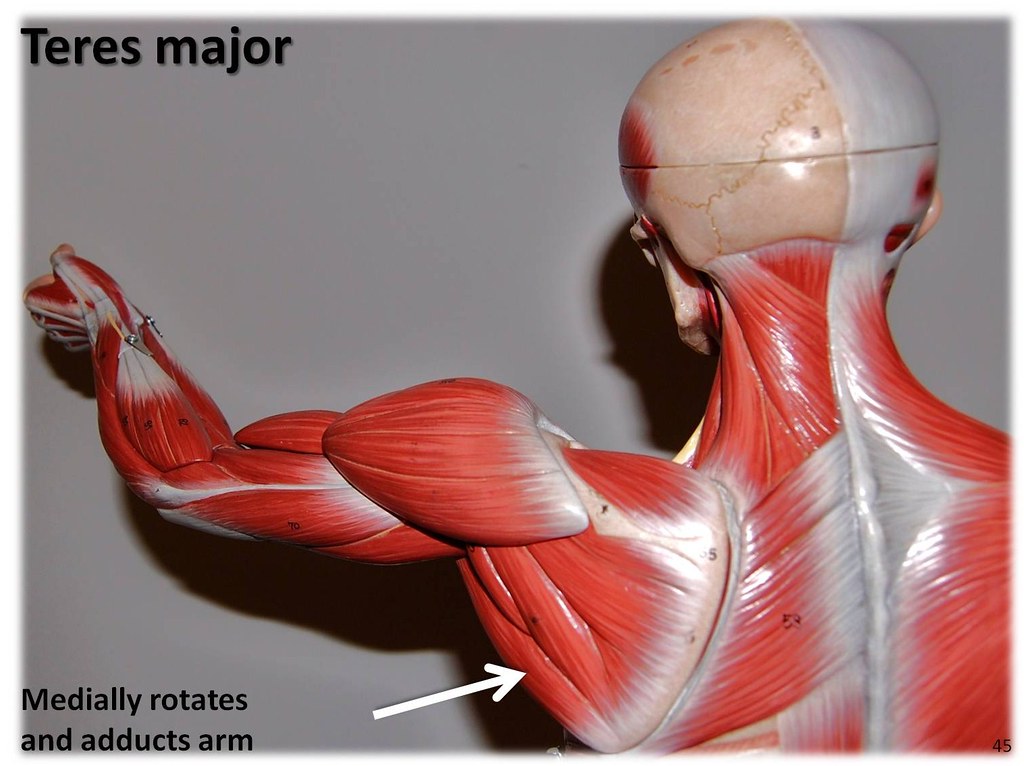
Teres major Muscles of the Upper Extremity Visual Atlas,… Flickr
Dorsal surface of inferior angle of scapula. Insertion. Medial lip of intertubercular groove of humerus. Action. Adducts and medially rotates arm. Innervation. Lower subscapular nerve (C6 and C7) (C6, C7) Arterial Supply. Subscapular and circumflex scapular arteries.